Basic JavaScript Concepts.
A Comprehensive Guide to Basic JavaScript Concepts
What is the difference between words and Keywords in JavaScript?
Word.
Anything that doesn't have a particular meaning in JavaScript is called a word.
For example.
my_Name, my_Age, my_Gender, num, x, y, z, a, b ,c
They all are words 👆
Keyword.
Keywords in JavaScript are words with assigned tasks and have some meanings.
// For example
let
const
if
else if
while
break
this
async
// They all are keywords as they have some meaning in JavaScripy.
What are variables & constants in JS?
What are variables?
The variable is something that changes.
Variables in programming?
In programming, if you want to store some data or information then you need variables that help you to store your data or information. You can change their values and update them as well.
Types of Variables in JS.
In JavaScript, you can declare or initialize variables in two ways.
let
var
What are constants in JS?
The constant is something that never changes.
Constant in JS?
In JavaScript, you can declare constant in only one way that is with const. You can never update const values and you can't redeclare them.
What is Undefined & Not defined?
Let's understand this with the help of an example.
Undefined.
If you have a variable in JS that you have declared but you didn't assign it a value. Then you console.log it and an error appears called the value of your variable is undefined. That means that JS finds your variable but doesn't find any value assigned to it.
// for exmaple
let my_Name;
console.log(my_Name); //undefined
Not defined.
Assuming you haven't declared and initialized the my_Age variable, attempting to log it will result in a not-defined error.
// for example
console.log(my_Age); // notdefined
Hoisting in JavaScript?
Hoisting in JavaScript is a behavior where variable and function declarations are moved to the top of their containing scope during the compile phase before the code is actually executed. This means that you can use a variable or a function before it has been declared.
console.log(myVariable); // Output: undefined
var myVariable = 10;
In the above code, myVariable is hoisted to the top of its scope, but its value is not yet defined. So, when you try to console.log(myVariable), it prints undefined.
Similarly, with functions.
myFunction(); // Output: "Hello!"
function myFunction() {
console.log("Hello!");
}
In this case, myFunction is hoisted to the top of its scope, so you can call it before its actual declaration in the code.
Data types in JS?
In JavaScript, there are two types of data.
Primitive data types.
Reference data types.
Primitive Data Types.
In the primitive data type, we have the following data types.
String
Number
Boolean
Undefined
Null
BigInt (ES11)
Symbol (ES6)
Reference Data Types.
In the reference data type, we have the following data types.
Functions
Arrays
Objects
Class (ES6)
Loops in JS?
In JavaScript, loops are control structures that allow you to repeatedly execute a block of code as long as a specified condition is true.
There are different types of loops in JS, but on the basis of JavaScirpt, we will talk about for loop and while loop.
for loop.
for loop consists of three parts.
The starting point of the loop.
The endpoint.
The interaction you want to make.
// for example
for(let i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
console.log(i*2)
}
// output : table of 2 printed.
While loop.
While loop also consists of three parts same as for the loop but their order is different
// for example
/*
starting point;
while(condition the must be false in future){
// print the value
The change you want to made.
}
*/
let a = 1;
while(a <= 10){
console.log(a*3);
a++;
}
// output : table of three printed
Functions in JS?
A function is mainly used for three things.
If you want to reuse your code.
If you want your code to run later in the future when you need it.
if you want to run your code with new inputs every time.
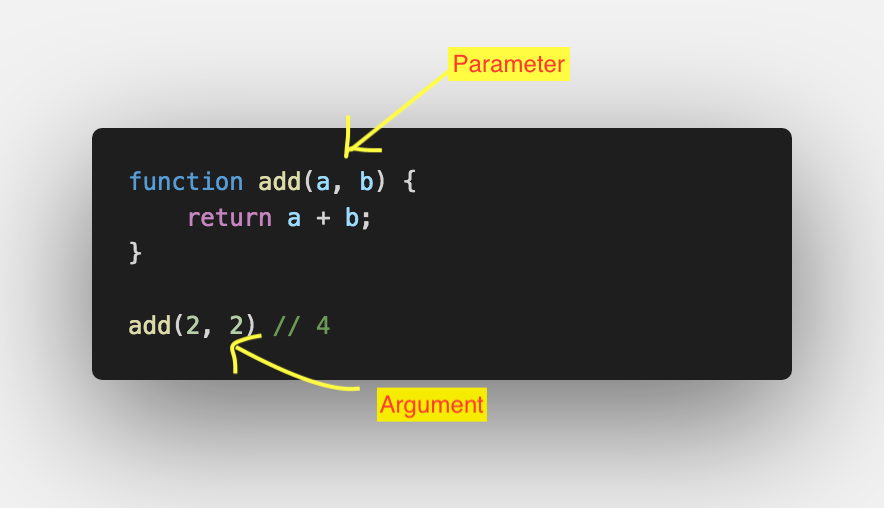
Parameters in function.
Variables that store the value of arguments are called parameters.
Arguments in function.
Arguments in function are nothing but real value that you have passed every time you call the function.
In how many ways we can write functions in JS?
There are six styles in which we can write our functions in JS. Three styles come in ES6 and three come in ES6 versions.
Function Declaration
Function Expression
Arrow Function(ES6)
Arrow Function with Implicit Return (ES6)
Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE)
Function inside an object
Let's create a simple function in JS.
// Lets do this with function decleration first.
function std_Details(name, age, profession){
return `name: ${name}, age: ${age}, profession: ${profession}`;
}
console.log(std_Details("Muhammad Shakir",22,"Front-end Dev"));
// lets do this funciton expression
let std_Details = funciton(name,age,depart){
return `name: ${name}, age: ${age}, depart: ${depart}`;
}
console.log(std_Details("Muhammad Haris",22,"Software Engineering"));
// let do this with arrow funciton : My Favorite😁
let std_Details = (name, email, std_ID) => {
return `name: ${name}, email: ${email}, std_ID: ${std_ID}`;
}
console.log(std_Details("Muhammad Shakir","xyz@gmail.com",77));
Arrays in JS?
An array is a type of Data Structure, that stores multiple values of multiple data types. You can also call it a group of values. Array use index numbers to store values and index number starts from 0 to nth. An index is a counting to the array.
// for example
let ary = ['Muhammad Shakir',22,'xyz@gmail.com'];
console.log(ary[0]); // Muhammad Shakir
console.log(ary[1]); // 22
console.log(ary[2]); // xyz@gmail.com
Objects in JS?
Let’s understand it with an example.
If you want to store multiple data of multiple persons let’s say names of different persons then here you can use array.
But if you want to store multiple data of a single person in a key-value pair then here you can use Objects.
Types of Objects.
Blank Objects.
Filled Objects.
// for example
let subDetails = {
name: 'Software Engineering',
code: 'SE-101',
creditHours: 3.5
}
// lets print the value of array.
console.log(subDetails.name); // Software Engineering
console.log(subDetails.code); // SE-101
console.log(subDetails.creditHours); // 3.5
Methods in JS?
A property in an object whose value is a function is called a method.
// lets create a calculator obj and inside it's diff methods.
let calculator = {
sum(x,y){
return x + y
},
sub(x,y){
return x - y
}
}
// for accessing the methods.
console.log(calculator.sum(4 , 5)); // 9
console.log(calculator.sub(5 , 4)); // 1